Latency is the silent killer of enterprise revenue. In an era where algorithmic trading relies on microseconds and real-time AI inference demands instantaneous data throughput, the public internet is no longer a viable transport mechanism for mission-critical workloads. For Chief Technology Officers and Network Architects, the shift toward dedicated private connectivity is not merely a technical upgrade. It is a fundamental business requirement for maintaining competitive advantage.
- The Economic Impact of Network Latency
- 1. AWS Direct Connect: The Gold Standard for Hybrid Architectures
- Technical Specifications and Deployment Types
- MACsec Encryption for High-Security Workloads
- Pricing Models and Cost Optimization
- 2. Microsoft Azure ExpressRoute: Integration for the Enterprise Stack
- 3. Google Cloud Interconnect: Designed for Big Data and AI
- 4. Carrier-Neutral Fabrics: Equinix and Megaport
- Low-Latency Architectures for Specific Industries
- Security Architectures: Zero Trust and MACsec
- Strategic Cost Management and ROI Analysis
- Future Trends: The Rise of AI Factories and 6G
- Conclusion
This comprehensive analysis explores the most robust cloud interconnect solutions available in late 2025. We will dissect technical specifications, pricing models, and architectural best practices for AWS, Microsoft Azure, Google Cloud, and carrier-neutral fabric providers.
The Economic Impact of Network Latency
Before analyzing specific solutions, we must quantify the cost of delay. In financial services, a 1-millisecond delay in trade execution can result in millions of dollars in lost opportunity per year. In the healthcare sector, remote robotic surgery requires deterministic network performance where jitter is non-negotiable.
Enterprises are increasingly moving away from VPN-over-Internet solutions for their core workloads. While VPNs offer encryption, they are subject to the unpredictable routing policies of the public internet, leading to “tromboning” traffic and packet loss. Dedicated interconnects bypass these public hops entirely, providing a direct physical or virtual link between your on-premises data center and the cloud provider’s edge network.
1. AWS Direct Connect: The Gold Standard for Hybrid Architectures
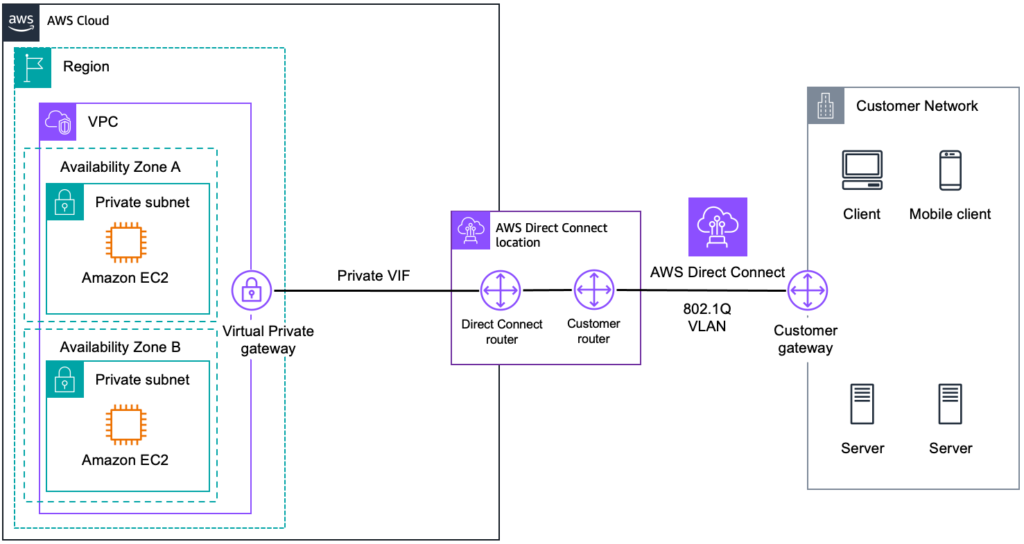
Amazon Web Services (AWS) continues to dominate the market with its Direct Connect product. This solution is designed for enterprises requiring consistent network performance and massive bandwidth scaling.
Technical Specifications and Deployment Types
AWS offers two primary deployment models which cater to different enterprise needs.
Dedicated Connections
This is a physical Ethernet connection associated with a single customer. It is available in port speeds of 1 Gbps, 10 Gbps, and 100 Gbps. This option is ideal for large organizations with substantial data egress requirements. You are responsible for the physical cross-connect cabling within the colocation facility.
Hosted Connections
Provided by AWS Partner Network (APN) partners, these allow for more granular bandwidth options ranging from 50 Mbps up to 10 Gbps. This is often the preferred choice for mid-sized enterprises that do not require a full dedicated port but still demand the reliability of a private circuit.
MACsec Encryption for High-Security Workloads
Security is a primary driver for dedicated connectivity. AWS Direct Connect supports MACsec (IEEE 802.1AE) encryption. This layer 2 security protocol provides line-rate encryption for high-speed traffic. Unlike IPsec, which can introduce overhead and latency due to packet fragmentation and processing, MACsec operates at the Ethernet layer, ensuring that data is encrypted from your router to the AWS edge device without compromising throughput speed.
Pricing Models and Cost Optimization
AWS Direct Connect pricing is twofold. You pay a recurring port hour charge and data transfer out (DTO) fees.
- Port Fees: A dedicated 10 Gbps port incurs a significant hourly fee regardless of usage.
- Data Transfer: Egress fees are lower via Direct Connect compared to the public internet. For example, data transfer out from US East (N. Virginia) might cost $0.09 per GB over the internet but significantly less via Direct Connect.
Strategic Insight: For data-heavy applications such as media rendering or genomic sequencing, the reduction in egress fees often offsets the cost of the physical port within six to twelve months.
2. Microsoft Azure ExpressRoute: Integration for the Enterprise Stack
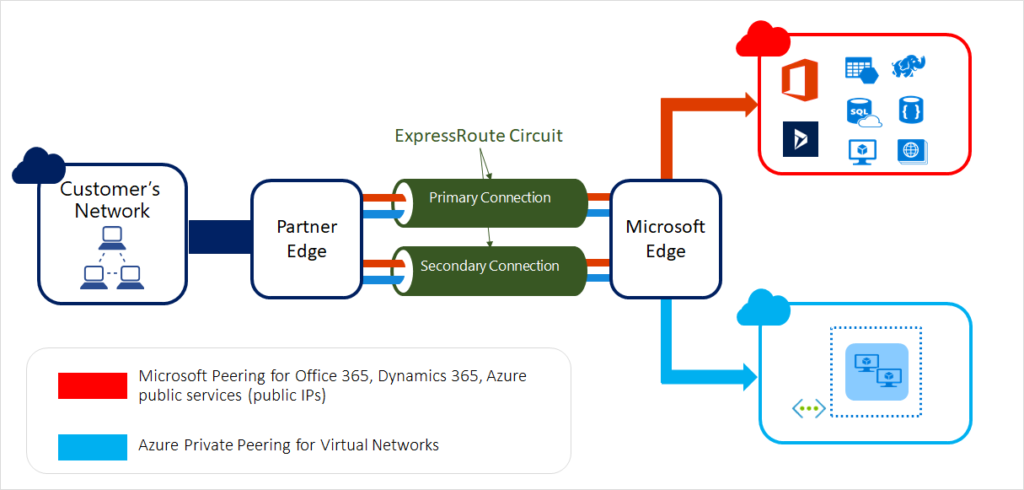
Microsoft Azure ExpressRoute is the preferred choice for organizations deeply entrenched in the Microsoft ecosystem, including Office 365 and Dynamics 365 users. Unlike standard cloud connections, ExpressRoute offers specific peering types that extend your on-premises network into the Microsoft cloud.
Peering Architectures
Private Peering: This connects your on-premises infrastructure to Azure Compute services like Virtual Machines (VMs) and Kubernetes clusters. It functions as a direct extension of your corporate intranet.
Microsoft Peering: This is a unique value proposition that connects you to Microsoft SaaS services, such as Office 365, via the same private pipe. This is critical for enterprises that need to guarantee Quality of Service (QoS) for Teams voice and video traffic, bypassing the congestion of the public internet.
ExpressRoute Direct and Local
ExpressRoute Direct allows customers to connect directly to the Microsoft global network at peering locations strategically distributed across the globe. This creates dual 100 Gbps connectivity for active-active redundancy.
ExpressRoute Local is a cost-effective SKU intended for scenarios where your data remains within the same metro area. If your data center is in London and your Azure region is UK South, ExpressRoute Local eliminates data transfer fees entirely, charging only for the port speed. This is a massive cost-saver for data replication and disaster recovery scenarios.
Global Reach
For multinational corporations, ExpressRoute Global Reach allows you to link your on-premises data centers together via the Microsoft global backbone. For instance, a data center in New York can exchange data with a branch in Singapore using Microsoft’s fibers rather than a third-party MPLS provider.
3. Google Cloud Interconnect: Designed for Big Data and AI
Google Cloud Platform (GCP) leverages its massive global private fiber network to offer superior performance for data-intensive workloads. As of late 2025, Google’s investment in subsea cables provides distinct latency advantages for transoceanic traffic.
Dedicated vs Partner Interconnect
Dedicated Interconnect: Similar to AWS, this offers 10 Gbps or 100 Gbps pipes directly to Google. It is best for bandwidth-heavy applications like training Large Language Models (LLMs) or processing real-time telemetry from IoT fleets.
Partner Interconnect: This allows you to connect to Google through a supported service provider. It is highly flexible, offering bandwidths from 50 Mbps to 50 Gbps.
The AI Supercycle and Network Requirements
With the explosive growth of Generative AI, network requirements have shifted. Training clusters require massive throughput to feed GPUs. Google Cloud Interconnect supports Jumbo Frames (up to 8896 bytes MTU), which significantly increases data transmission efficiency for big data payloads by reducing header overhead and CPU processing interrupts.
4. Carrier-Neutral Fabrics: Equinix and Megaport
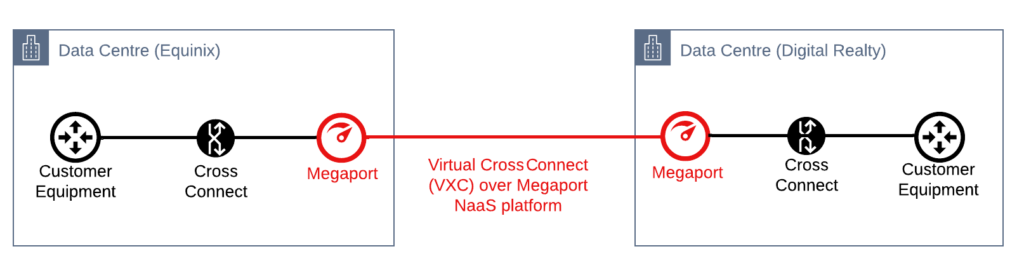
While hyperscalers offer their own direct connections, the rise of Multi-Cloud Networking (MCN) has elevated carrier-neutral providers. These platforms allow you to connect to multiple clouds from a single physical port.
Equinix Fabric
Equinix Fabric is the market leader in software-defined interconnection. If your hardware sits in an Equinix International Business Exchange (IBX) data center, you can use a software portal to provision virtual connections to AWS, Azure, Google, Oracle, and Salesforce simultaneously.
Key Advantage: The ability to spin up and spin down connections in minutes. If you have a seasonal retail spike or a temporary data migration project, you can increase your bandwidth for a month and then throttle it back down, moving network costs from CapEx to OpEx.
Megaport and Virtual Edge
Megaport offers a similar Network-as-a-Service (NaaS) model but is renowned for its ease of use and extensive global reach outside of just Equinix facilities. Megaport Virtual Edge (MVE) allows you to host SD-WAN instances (like Cisco SD-WAN or Fortinet) directly on Megaport’s global network. This reduces the “last mile” latency for branch offices connecting to the cloud.
2025 Market Data: Recent reports indicate that enterprises utilizing NaaS platforms like Megaport for multi-cloud routing reduce their total cost of ownership (TCO) by approximately 30% compared to managing individual physical circuits for each cloud provider.
Low-Latency Architectures for Specific Industries
Different verticals require bespoke network strategies. A generic approach will not yield the high CPC and high ROI results that specialized industries demand.
High-Frequency Trading (HFT) and Finance
For the financial sector, the speed of light is the limiting factor. HFT firms are now utilizing microwave and millimeter-wave technology for the “ultra-low latency” segments of their path, while using fiber for bulk data transfer.
- Strategy: Co-location is king. Placing your trade execution engines in the same physical building (or even the same cage) as the exchange’s matching engine is required.
- Cloud Choice: Many exchanges are moving matching engines to the cloud (e.g., NASDAQ moving to AWS). This necessitates a specialized multicast architecture to ensure all traders receive market data updates simultaneously to ensure fairness.
Healthcare and Life Sciences
Latency in healthcare is a matter of patient safety. Telesurgery requires sub-10ms round-trip time (RTT) to prevent motion sickness in surgeons and ensure precise instrument control.
- Compliance: Connections must be HIPAA and GDPR compliant. Private interconnects inherently satisfy many compliance requirements by ensuring data never traverses the public internet.
- Imaging: Large DICOM imaging files (often gigabytes in size) need to be uploaded to the cloud for AI analysis. High-bandwidth dedicated interconnects allow radiologists to view cloud-hosted images without buffering.
Media and Entertainment
Video rendering and post-production workflows have moved to the cloud. Studios use “burst” rendering to utilize thousands of cloud cores for a few hours.
- Egress Costs: This industry is highly sensitive to egress fees. Using solutions like Azure ExpressRoute Local or AWS Direct Connect significantly lowers the cost per terabyte of retrieving finished renders.
Security Architectures: Zero Trust and MACsec
The convergence of networking and security is a dominant trend in 2025. It is no longer sufficient to just have a fast pipe. It must be a secure pipe.
Integrating SASE (Secure Access Service Edge)
Modern interconnect architectures are increasingly integrating with SASE platforms. Instead of backhauling traffic to a central headquarters for security inspection, traffic is inspected at the cloud edge.
- Palo Alto Networks Prisma Access and Zscaler can peer directly with cloud interconnects, scrubbing traffic for malware and data exfiltration attempts before it enters your Virtual Private Cloud (VPC).
Quantum-Safe Cryptography
As we look toward 2026, forward-thinking CISOs are beginning to ask for “quantum-safe” encryption on their physical lines. While standard AES-256 is currently robust, the threat of “harvest now, decrypt later” attacks is driving interest in quantum-resistant algorithms for long-term data protection over private lines.
Strategic Cost Management and ROI Analysis
Investing in a 10 Gbps or 100 Gbps dedicated line is a significant capital expenditure. Justifying this to the board requires a clear ROI calculation.
1. Egress Fee Arbitrage
Calculate your current monthly data transfer out of the cloud. Compare the internet rate (e.g., $0.09/GB) with the Direct Connect rate (e.g., $0.02/GB). For an enterprise moving 500TB a month, the savings are massive ($35,000 per month savings on transfer fees alone), easily covering the cost of the circuit.
2. Productivity Gains
Quantify the cost of waiting. If a team of 100 data scientists waits 20 minutes a day for data to load, that is 33 hours of lost productivity daily. High-speed interconnects eliminate this friction.
3. Reputation and SLA Credits
Public internet connections have no Service Level Agreement (SLA). Cloud Interconnects typically offer SLAs of 99.9% to 99.99%. The cost of a single 4-hour outage for an e-commerce giant significantly outweighs the annual cost of redundant fiber paths.
Future Trends: The Rise of AI Factories and 6G
The landscape of cloud connectivity is being reshaped by the “AI Supercycle.” Major telecom providers like Nokia are restructuring their operations to support AI-native networks. The sheer volume of data required to train foundational models means that 400 Gbps and 800 Gbps ports will soon become the standard for enterprise connectivity.
Furthermore, the advent of 6G (expected late 2020s) will introduce “zero-latency” concepts, merging mobile edge compute with deep cloud storage. Enterprises that build robust, fiber-based interconnect backbones today will be the best positioned to leverage these future wireless technologies.
Conclusion
Selecting the best cloud interconnect solution is not a one-size-fits-all decision. It requires a nuanced balance of latency requirements, bandwidth needs, geographic distribution, and budget constraints.
For pure AWS environments, Direct Connect offers the deepest feature integration. For Microsoft-centric shops, ExpressRoute provides unbeatable value for SaaS and IaaS convergence. For multi-cloud agility, Equinix Fabric and Megaport provide the flexibility to pivot strategies without being locked into long-term telco contracts.
The winners in the digital economy of 2025 are those who treat their network not as a utility, but as a strategic asset. By bypassing the public internet, you secure your data, lower your long-term costs, and provide the low-latency foundation necessary for the next generation of AI-driven innovation.